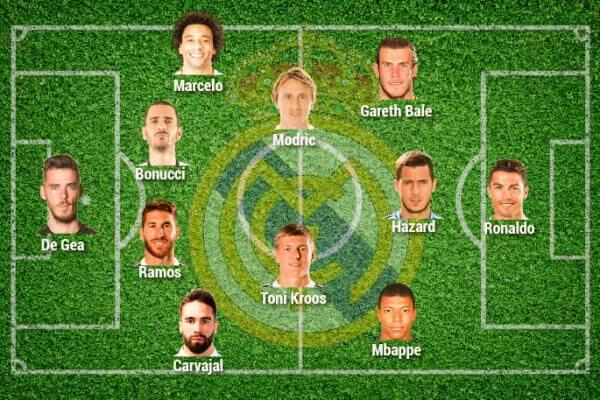
Cùng FO4VN ─ Đội hình Chiến thuật FO4 ─ Tra cứu cầu thủ FO4 khám phá về các lôi đài và cầu thủ trong tựa game huyền thoại FIFA Online 4 (FO4). Trang web FO4VN là nơi bạn có thể tìm hiểu thông tin về đội hình, kỹ năng cầu thủ, cách sắp xếp đội hình chiến thuật, và nhiều nội dung hấp dẫn khác.
Wood Storks: Guardians of Wetland Ecosystems
In Corkscrew Swamp Sanctuary, the historical wood stork (Mycteria americana) colony flourishes amidst the old growth bald cypress forest. This sanctuary has become the most celebrated nesting ground for these majestic creatures in our nation. The continuous monitoring by Audubon since 1958 has provided invaluable data on wood stork nesting, making it the longest-running study of its kind in the country.
Wood Storks and the Health of Wetlands
The nesting success of wood storks in the Everglades relies heavily on the hydrology of the surrounding wetlands. The duration of standing water and the rate at which water recedes during the dry season play a crucial role in the availability of aquatic prey, such as small fish and crayfish. These prey species provide the essential energy needed for nest building, egg incubation, and the fledging of young wood storks. Due to their dependence on specific wetland conditions, wood storks are considered an indicator species for Everglades restoration efforts.
During the wet season (June-September), flooding occurs, connecting numerous wetlands and allowing for the dispersal and multiplication of aquatic fauna. As the dry season (October-May) ensues, the gradual recession of surface water creates isolated depressions that harbor concentrated populations of aquatic organisms. This abundance of prey attracts wood storks, among other wading birds, otters, and alligators. The shallow waters (less than 16 inches) become a tactile feeding ground for wood storks.
The Impact of Human Development on Wood Stork Nesting
In recent decades, extensive drainage and fragmentation of wetlands have occurred throughout South Florida. The construction of canals, ditches, and roads has led to significant changes in the landscape and a subsequent decline in wood stork nesting across the Everglades. The Everglades wood stork population has also seen a decline as a result of these modifications. Restoring the wetlands to their natural, pre-drainage state is predicted to increase wood stork breeding efforts and population in the region.
The Decline of the Corkscrew Wood Stork Colony
Scattered records of wood stork nesting at Corkscrew date back to 1914, and the National Audubon Society has been monitoring the colony since 1958. Unfortunately, nesting efforts have significantly declined over the years. Productivity, measured by the number of chicks fledged, has dropped from an average of 5,450 chicks per year in the first decade of monitoring to just 287 chicks per year in the most recent decade. In the past 10 years, wood storks have only nested at the Corkscrew colony twice (in 2009 and 2014).
Audubon’s Western Everglades Research Center is diligently working to understand the decline of the Corkscrew Wood Stork colony. Their research findings are crucial for informing conservation policies and guiding wetland restoration projects that will benefit not only wood storks but also other native wildlife.
Join FO4VN ─ Đội hình Chiến thuật FO4 ─ Tra cứu cầu thủ FO4 to learn more about the fascinating world of wood storks and stay up-to-date with the latest happenings in the FIFA Online 4 (FO4) gaming universe. Visit FO4VN ─ Đội hình Chiến thuật FO4 ─ Tra cứu cầu thủ FO4 for all your FO4 needs!